Properties
- Size: 100 μg
- Appearance: Solution
- Formulation: 70 μM monomeric AS in PBS, pH 7.4 with 700 μM DA. Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
- Reconstitution: Not applicable
- Purification: Purified by ion-exchange chromatography.
- Purity: > 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
- Endotoxins: ND
- Storage and Stability: It is recommended to freeze aliquots at - 80°C for up to 12 months under sterile conditions. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
- Shipping: This product is shipped with dry ice in Europe, may vary elsewhere. Please inquire the shipping cost.
- Cite This Product: Human recombinant Alpha-synuclein monomer with DA (BRINDx, Argentina, REF: BRX-1005).
Biological Descriptions
- Background: Alpha-synuclein is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the SNCA gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release. It is abundant in the brain, while smaller amounts are found in the heart, muscle and other tissues. In the brain, alpha-synuclein is found mainly in the axon terminals of presynaptic neurons. Within these terminals, alpha-synuclein interacts with phospholipids and proteins. Presynaptic terminals release chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, from compartments known as synaptic vesicles. The release of neurotransmitters relays signals between neurons and is critical for normal brain function. In Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies, insoluble forms of alpha-synuclein accumulate as inclusions in Lewy bodies. Familial Parkinson's disease is associated with mutations in the alpha-synuclein (SNCA) gene. In the process of seeded nucleation, alpha-synuclein acquires a cross-sheet structure similar to other amyloids. The human alpha-synuclein protein is made of 140 amino acids. An alpha-synuclein fragment, known as the non-amyloid beta component (NAC) of Alzheimer's disease amyloid, originally found in an amyloid- enriched fraction, was shown to be a fragment of its precursor protein, NACP. It was later determined that NACP was the human homologue of Torpedo synuclein. Therefore, NACP is now referred to as human alpha- synuclein.
- Research area: Neuroscience. Neurogenerative disorders. Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease. Synucleinopathies. Tauopathies.
- Cellular Localization: Cytoplasm, Membrane, Nucleus. Synonyms: synuclein alpha, NACP, PARK1, PARK4, PD1. Data Base: Gene ID: 6622 [NCBI].
- Accession: #P37840.
Product Data
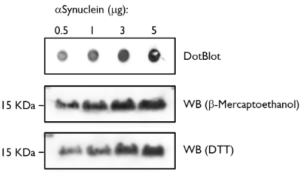
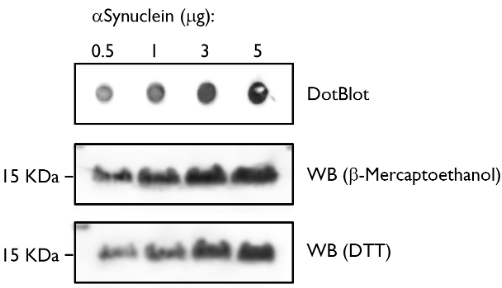
Dot Blot and Western Blot. Alpha-synuclein protein monomer.
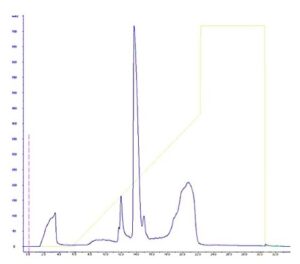
FPLC. Alpha-synuclein protein Chromatrogram purification . Elution of the protein by performing a NaCl concentration gradient up to 60%. The peak with the highest absorbance corresponds to the purified protein.
Applications
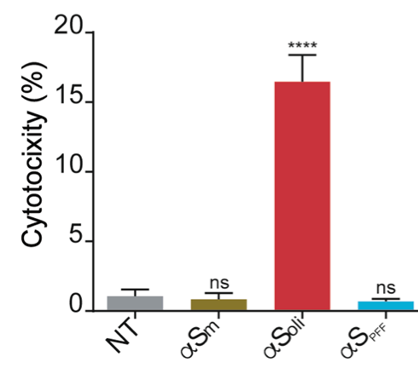
Alpha synuclein oligomers citotoxicity
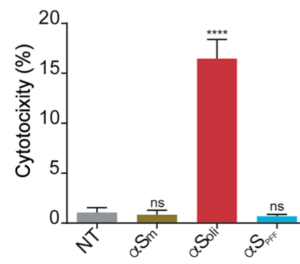 LDH cytotoxicity assay in SH-SY5Y cells after the addition of αS monomer, αS oligomers and αS PFF. The cytotoxicity signal was normalized to values obtained after addition of Triton X-100. One-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. ****p < 0.0001 vs NT.
LDH cytotoxicity assay in SH-SY5Y cells after the addition of αS monomer, αS oligomers and αS PFF. The cytotoxicity signal was normalized to values obtained after addition of Triton X-100. One-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. ****p < 0.0001 vs NT.
References
1. Repurposing doxycycline for synucleinopathies: remodelling of α-synuclein oligomers towards non-toxic parallel beta-sheet structured species. Scientific Report (Nature). DOI: 10.1038/srep41755.
2. Rifampicin and Its Derivative Rifampicin Quinone Reduce Microglial Inflammatory Responses and Neurodegeneration Induced In Vitro by α-Synuclein Fibrillary Aggregates. Cells. DOI: 10.3390/cells8080776.
3. Microglial glutamate release evoked by α-synuclein aggregates is prevented by dopamine. Glia. DOI: 10.1002/glia.23472.
4. Neuroprotective Effects of a Novel Demeclocycline Derivative Lacking Antibiotic Activity: From a Hit to a Promising Lead Compound. Celss. DOI: 10.3390/cells11172759.
5. CMT-3 targets different α-synuclein aggregates mitigating their toxic and inflammogenic effects. Scientific Report (Nature). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-76927-0.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.